Revealing Brain Waves in the moment - some interpretations
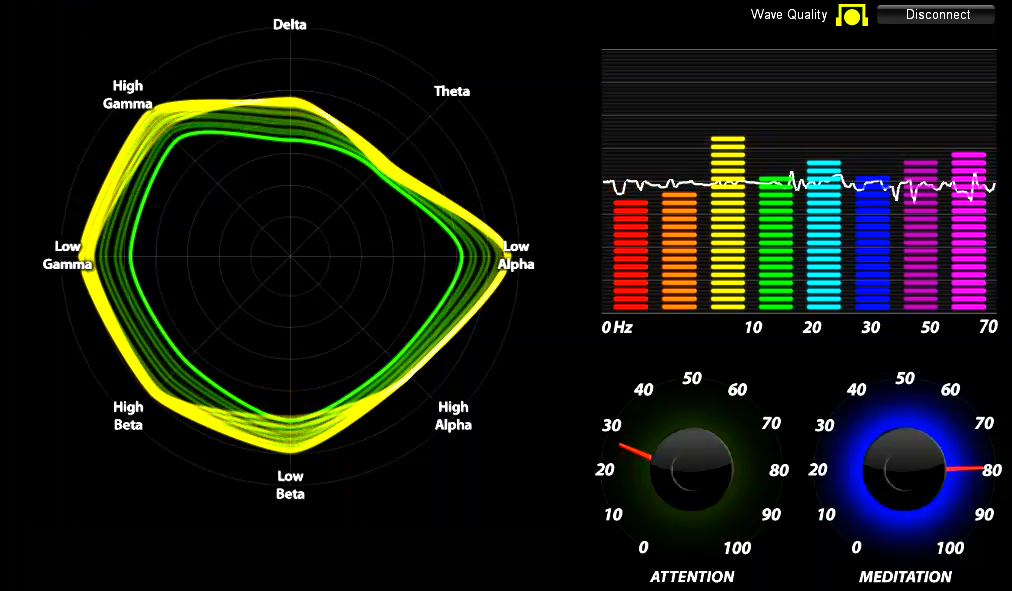
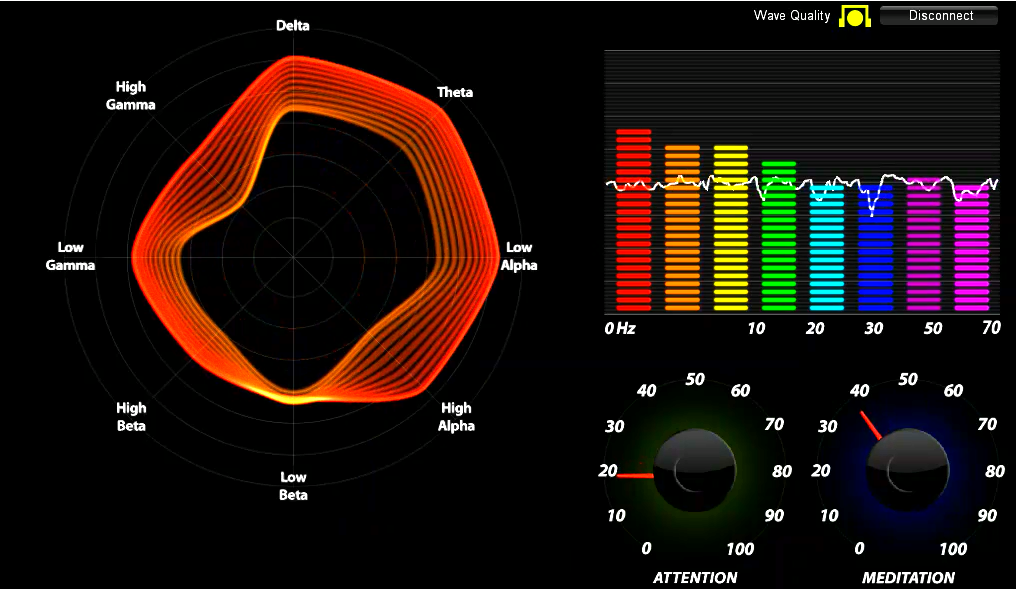
Brainwaves can reveal your emotions and state. The tracking on left is shown in real time from Neurosky systems
Brainwaves are a result of the electrical impulses produced as our brain cells communicate with one another. They reveal how we respond and function at a moment in time.
They can give us insights into:
our thought habits,
stress levels,
underlying mood
and overall brain function.
Our brainwaves change according to what we’re doing and feeling. When slower brainwaves are dominant we can feel tired, slow, sluggish, or dreamy. The higher frequencies are dominant when we feel wired, or hyper-alert.
The descriptions that follow are only broad descriptions - in practice things are far more complex, and brainwaves reflect different aspects when they occur in different locations in the brain.
Description of brainwave functions
A general description of our brain waves
Tracking the dominant colour
Note; The observations below the images reflect our own interpretation and are not to be used to inform clinical or medical protocols.
Brainwave speed is measured in Hertz (cycles per second) and they are divided into bands delineating slow, moderate, and fast waves. They are measured in hertz and are divided levels for convinience.
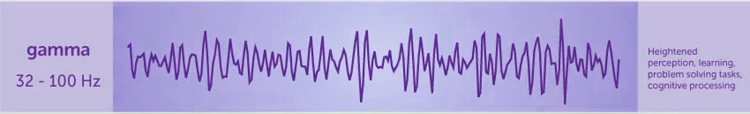
Gamma brainwaves are the fastest of brain waves (high frequency, like a flute), and relate to simultaneous processing of information from different brain areas. Gamma brainwaves pass information rapidly and quietly.
The most subtle of the brainwave frequencies, the mind has to be quiet to access gamma.
Gamma was dismissed as 'spare brain noise' until researchers discovered it was highly active when in states of universal love, altruism, and the ‘higher virtues’. Gamma is also above the frequency of neuronal firing, so how it is generated remains a mystery.
It is speculated that gamma rhythms modulate perception and consciousness, and that a greater presence of gamma relates to expanded consciousness.
It is responsible for cognitive functioning, learning, memory, and information processing.
Prominence of this wave leads to anxiety, high arousal, and stress;
Its suppression can lead to Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), depression, and learning disabilities.
In optimal conditions gamma waves help with attention, focus, binding of senses (smell, sight, and hearing), consciousness, mental processing, and perception.
Hi Gamma (45 - 100 Hz) found in simultaneous processing, linking ideas
Hi Gamma (45 - 100 Hz) found in states of altruism, and Empathy
low gamma (32 -40 Hz) Support cognitive functioning and mental processing, learning, memory, and information processing., binding of senses, and perception.
BETA WAVES (12 TO 38 HZ)
Beta brainwaves dominate our normal waking state of consciousness when attention is directed towards cognitive tasks and generally the outside world.
Beta is a ‘fast’ activity, when we are alert, attentive, engaged in problem solving, judgment, decision making, or focused mental activity.
Beta brainwaves are divided into three bands
Hi-Beta (Beta3, 22-38Hz) is high energy and highly complex thought, high arousal and excitement, Integrating new experiences.
It is also found in significant stress. Continual high frequency processing is not a very efficient way to run the brain, as it takes a great deal of energy, using up both physical and emotional resources.
Beta (Beta2, 15-22Hz) is high engagement or actively figuring something out. Found in sustained good performance and in stressful situations.
Lo-Beta (Beta1, 12-15Hz) described as quiet, musing and introverted concentration.
Continual high frequency processing is not a very efficient way to run the brain, as it takes a tremendous amount of energy.
Hi-Beta (Beta3, 22-38Hz) IT SIGNIFIES high arousal and excitement, AND SOMETIMES, high stress.
Beta (Beta2, 15-22Hz) is high engagement or actively figuring something out.
Lo-Beta (Beta1, 12-15Hz) FOUND IN QUIET CONCENTRATION', or musing and SMR focus.
SMR WAVES (12 TO 15 HZ)
The SMR frequency band (11-15 Hz) describes an alert, attentive state with relaxed physical movements, or stillness.
This training adapts the sleepy mind-wandering and habitual rumination found in Theta, or the ‘spinning’ or anxious waves of High Beta.
The Neurofeedback training protocol here aims to strengthen the quality of attention and the ability to sustain focus by building stronger neural networks (dlPFC and vlPFC link to limbic Pregenu Cingulate Cortex) which in turn promotes mind + brain + body coherence.
SMR protocol aims to inhibit Theta and High Beta, and reward Lo-Beta (SMR) at the at Cz or C4, based on the international 10-20 Brodmann scalp system.
It builds a sense of calm relaxation with alertness as well as builds physical motor accuracy and balance.
SMR (12-14 Hz) describes an aware and relaxed state
ALPHA (10 TO 12 hZ)
ALPHA WAVES (8 TO 12 HZ)
Alpha is ‘the power of now’, being present in the moment.
Alpha waves are dominant during quietly flowing thoughts, and in some meditative states. It is the resting state for the brain.
Alpha waves aid overall mental coordination, calmness, alertness, mind/body integration and learning.
They help us calm down when necessary and promote feelings of deep relaxation.
Alpha waves are found prominently in daydreaming, inability to focus, and being very relaxed.
If they are suppressed it can cause anxiety, high stress, and insomnia.
When they are optimal it leads to a relaxed state.
hIGH aLPHA (10 TO 12 hZ)
lOW aLPHA (8 TO 10 hZ)
THETA WAVES (3 TO 7 HZ)
Theta brainwaves occur most often in sleep but are also dominant in deep meditation.
Theta is our gateway to learning, memory, and intuition. In theta, our senses are withdrawn from the external world and focused on signals originating from within.
Theta is involved in daydreaming, a state we normally experience briefly as we wake up or drift off into sleep.
It informs intuition, offering insights into our unconscious stored memory and imaginings. It’s where we hold our ‘stuff’, our fears, troubled history, or bad dreams.
In an optimal state, theta helps in creativity, emotional connection, intuition, and relaxation. Theta waves have benefits of helping to improve our intuition and creativity, and making us feel more natural. Theta is also involved in restorative sleep.
If theta is in a suppressed state, it can indicate poor emotional awareness or rumination.
When theta waves are prominent; it can signify aspects of inattentiveness, depression, hyperactivity or impulsivity, inattentiveness or ADHD, .
HETA (4 - 7 hz) with lOW aLPHA (8-10 hZ)
Dominant tHETA (4 - 7 hz) with lOW aLPHA (8-10 hZ)
tHETA (4 - 7 hz) with lOW aLPHA (8-10 hZ) and Delta (0.5 - 3 Hz)
DELTA WAVES (.5 - 3 HZ)
Delta waves are the slowest waves in humans, strongly found in infants and young children. Loud brainwaves (low frequency and deeply penetrating, like a drum beat).
Healing and regeneration are stimulated in this state, and that is why deep restorative sleep is so essential to the healing process.
Delta waves suspend external awareness. generated in deepest meditation and dreamless sleep. They are the source of empathy.
They are associated with the deepest levels of relaxation and restorative, healing sleep. Adequate production of delta waves helps us feel completely rejuvenated and promotes the immune system, natural healing, and restorative/deep sleep.
Delta predominates in brain injuries, learning problems, inability to think, and severe ADHD.
If this wave is suppressed, it leads to an inability to rejuvenate the body and revitalize the brain, and poor sleep.
Infra-Low brainwaves (also known as Slow Cortical Potentials), are thought to be the basic cortical rhythms that underlie our higher brain functions. Very little is known about infra-low brainwaves. Their slow nature make them difficult to detect and accurately measure, so few studies have been done. They appear to take a major role in brain timing and network function.
This requires a clinical approach and QUEEG Brain Mapping.
INFRA-LOW (<.5HZ)
What your brainwaves mean to you
Our brainwave profile and our daily experience of the world are inseparable. When our brainwaves are out of balance, there will be corresponding problems in our emotional or neuro-physical health. Research has identified brainwave patterns associated with all sorts of emotional and neurological conditions. more...
More about Brain Waves Frequencies
The EEG (electroencephalogram) is used to measure the electrical changes produced by the pyramidal cells on the surface of the cortex.
The brain waves recorded by the EEG are measured in frequency (how many brain waves per second) and in amplitude (the electrical potential or how many cells fire at the same time at the same speed is expressed as voltage). The frequencies or brain speed correspond to particular mindsets as summarized in the following chart.
Neurofeedback training, particularly relating to attention difficulties. is interested in the frequencies between 4 and 20 cycles per second, or hertz.
The theta waves are slower brain waves in the range of 4 to 7 hertz. They are associated with a “tune-out mode”. The waves between 7 and 11 are called the alpha waves. They present a resting, daydreaming mindset.
The SMR brain waves (Sensory Motor Rhythm) refer to the waves in the 12 to 15 hertz range. They are associated with a calm but alert mental state. They allow the person to control their impulsivity while they give a feeling of quiet alertness. Barry Sterman first identified this specific frequency range, while working with cats. As he rewarded the cats to produce more SMR, their bodies were calm, but their brains were alert, ready for action. However, when he rewarded the cats to produce less SMR, the cats were twitchy and impulsive.
The brain waves between 15 and 20 hertz are called beta. They are necessary for the focused, analytical mind set necessary to solve problems. We see more of these waves when a person is learning a new task requiring mental effort, in comparison to doing a repetitive, already learned and mastered task
Over-arousal in certain brain areas is linked with anxiety disorders, sleep problems, nightmares, hyper-vigilance, impulsive behaviour, anger/aggression.
Under-arousal in certain brain areas leads to some types of depression, attention deficit, chronic pain and insomnia.
A combination of under-arousal and over-arousal is seen in cases of anxiety, depression and ADHD. more..
References:
1. Rowan's Primer of EEG (2nd Ed) 2016.
The Normal Adult EEG. P 39-66.
Lara V Marcuse MD et al, Assistant Professor Neurology and Co-Director of the Mount Sinai Epilepsy Center, The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, USA
2. EG-Based Brain-Computer Interface: Cognitive Analysis and Control Applications, 2019
3. Neuro Health
Neuro Facts, Neurofeedback
4. Neuro Clinic
Practice to increase your coherence baseline and improve your ability to take charge of your emotional reactions and well-being.